Quick links to article content:
What is E-Waste?
E-Waste Collection in Estonia: The Role of Eesti Elektroonikaromu
Types of E-Waste
Global Trends in E-Waste
E-Waste Policy in Estonia
Producer Responsibility under the WEEE Act in Estonia
Sustainable E-Waste Management in Estonia
Producer Obligations and the Necessity of Joining a Producer Responsibility Organization (PRO)
Joining Eesti Elektroonikaromu: Your Partner in Responsible E-Waste Management
Frequently asked questions on Electronic Waste Management in Estonia
Related materials
E-Waste collection points in Estonia
As one of the leading Producer Responsibility Organizations (PROs) in Estonia, Eesti Elektroonikaromu is steadfastly dedicated to the efficient management and recycling of all forms of electronic waste (e-waste) and batteries.
What is E-Waste?
E-waste, or electronic waste, refers to discarded electrical or electronic devices. This includes both “white goods,” such as refrigerators, washing machines, and microwaves, and “brown goods,” such as televisions, cameras, and radios.
Other categories include “gray goods,” such as computers, printers, and phones. Furthermore, all kinds of discarded batteries are also considered e-waste.
E-waste is one of the fastest-growing waste streams worldwide due to the rapid turnover of electronic and electrical equipment in today’s highly digital and interconnected world. If not managed properly, e-waste can have serious environmental and health impacts due to its content of toxic substances such as mercury, lead, and cadmium.
However, it can also be a valuable resource, as e-waste contains precious metals like gold, silver, and palladium that can be recovered and reused.
E-Waste Collection in Estonia: The Role of Eesti Elektroonikaromu
Eesti Elektroonikaromu plays a pivotal role in organizing the collection of e-waste in Estonia. Here’s how it works.
Network of Collection Points
Eesti Elektroonikaromu has established an extensive network of collection points across Estonia where individuals and businesses can drop off their e-waste for free. This includes smaller collection bins for portable batteries and larger collection containers for all types of e-waste.
Take-Back System
Eesti Elektroonikaromu works with retailers to implement a take-back system where customers can return old or end-of-life electrical and electronic equipment when they purchase new items, regardless of whether the old item is of the same type as the new one.
Collection from Businesses
For larger businesses, institutions, or municipalities with significant amounts of e-waste, Eesti Elektroonikaromu offers a direct collection service. They arrange for the pickup and transportation of e-waste directly from these premises.
Special Collection Events
In addition to these regular services, Eesti Elektroonikaromu also organizes special collection events in different locations to encourage local communities to dispose of their e-waste responsibly.
In conclusion, Eesti Elektroonikaromu, as a leading PRO in Estonia, not only takes care of the efficient management and recycling of e-waste and batteries, but also helps to educate the public about the importance of proper e-waste disposal, contributing to a more sustainable Estonia.
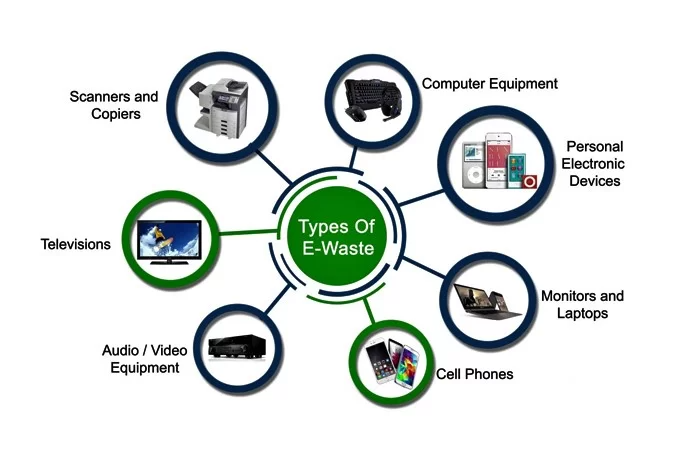
Types of E-Waste
Electronic waste, or e-waste, includes various forms of waste from discarded electronic devices that have reached the end of their life. These can be broadly categorized into the following groups:
Consumer Electronics: This includes everyday electronic items used by individuals, such as televisions, computers, laptops, tablets, mobile phones, cameras, and audio devices. It also encompasses wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers.
Home Appliances: These are larger devices typically found in households, including refrigerators, washing machines, dryers, dishwashers, microwave ovens, and air conditioners.
IT and Telecommunication Equipment: This category includes devices like servers, routers, switches, and other related hardware used primarily in business and industry settings.
Batteries: All types of used and discarded batteries, including those from electronic devices, vehicles, and industrial use, are considered e-waste due to the special handling required for their disposal.
Global Trends in E-Waste
The global trends in e-waste are characterized by several key developments:
Increasing Volumes: Due to rapid technological advancements, shorter product lifecycles, and growing consumer demand, the volume of e-waste generated globally is increasing at an unprecedented rate. According to the Global E-waste Monitor 2020, a record 53.6 million metric tonnes of e-waste was generated worldwide in 2019, an increase of 21% in just five years.
Low Recycling Rates: Despite the growth in e-waste, global recycling rates remain relatively low. The Global E-waste Monitor reports that just 17.4% of 2019’s e-waste was collected and properly recycled. This implies that a vast amount of valuable and potentially hazardous materials remains unaccounted for.
Legislation and Producer Responsibility: Many countries are implementing stricter legislation to address e-waste. The concept of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), where manufacturers are held responsible for the end-of-life management of their products, is becoming more prevalent.
Emerging Health and Environmental Concerns: The improper disposal of e-waste poses significant environmental and health risks due to the hazardous materials they often contain. Consequently, there’s growing global awareness about the environmental impact of e-waste and the necessity for its proper management.
Circular Economy and Resource Recovery: There’s increasing recognition of the value within e-waste. It is seen as a source of secondary raw materials, including precious metals, which, if recovered, can decrease reliance on mining and reduce the environmental footprint associated with the production of new electronics.
In summary, the global trends in e-waste are characterized by rising volumes and increasing recognition of the environmental and health risks associated with improper e-waste disposal. At the same time, there is a growing emphasis on legislation, producer responsibility, and the principles of a circular economy to manage and reduce e-waste.

E-Waste Policy in Estonia
In Estonia, the policy on electronic waste (e-waste) is primarily guided by the EU’s Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive, which Estonia has adopted into its national legislation. This policy places a strong emphasis on the principles of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), aiming to reduce e-waste and promote its proper treatment and recycling.
Under the WEEE regulations in Estonia, all producers and importers of electronic and electrical equipment are required to register their products, provide information on the quantities placed on the market, and report on the waste collected and treated.
They must also ensure that their products are appropriately labeled to indicate that they should not be disposed of with unsorted municipal waste and that they are separately collected.
Producer Responsibility under the WEEE Act in Estonia
The WEEE Act in Estonia places a significant responsibility on the shoulders of producers. This includes manufacturers, importers, and sellers of electronic and electrical equipment. These entities are legally obligated to ensure the proper management of e-waste derived from their products. This involves the collection, transportation, and proper disposal of the e-waste, either by treating it themselves or by delegating these tasks to a certified waste management company or a Producer Responsibility Organization (PRO).
Role of Eesti Elektroonikaromu in Sustainable E-Waste Management in Estonia
As one of the leading PROs in Estonia, Eesti Elektroonikaromu plays a critical role in implementing these producer responsibilities and advancing sustainable e-waste management in the country. The organization facilitates the collection, recycling, and responsible disposal of all types of e-waste and batteries on behalf of its member companies, thereby helping them fulfill their obligations under the WEEE regulations.
Eesti Elektroonikaromu operates a vast network of collection points and cooperates with retailers to offer take-back services, ensuring that end-of-life electronic devices and batteries are conveniently and freely returned. Furthermore, the organization arranges for the proper treatment of collected e-waste, promoting the recovery of valuable materials and the safe disposal of hazardous substances.
In addition to its operational activities, Eesti Elektroonikaromu also plays a significant role in raising awareness about e-waste issues and promoting responsible e-waste management among consumers and businesses.
Through its efforts, the organization contributes to the broader goals of environmental protection, resource efficiency, and sustainable development in Estonia.
In conclusion, e-waste policy in Estonia, driven by the WEEE Directive and the principle of Extended Producer Responsibility, places a strong emphasis on the responsible management of e-waste. In this context, Eesti Elektroonikaromu serves as a key player, helping producers meet their legal obligations and advancing sustainable e-waste management in the country.

Producer Obligations and the Necessity of Joining a Producer Responsibility Organization (PRO)
The necessity for producers, dealers, retailers, and web-shops to join a PRO stems from their legal obligations under the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) regulations. These regulations stipulate that producers are responsible for the end-of-life management of the electrical and electronic products they place on the market.
These responsibilities include collection, recycling, recovery, and environmentally sound disposal of e-waste. They also include the provision of information about the quantities of products placed on the market and the quantities of waste collected and treated.
Managing these obligations independently can be a complex and resource-intensive task, particularly for businesses that do not specialize in waste management. That’s where a PRO like Eesti Elektroonikaromu comes in.
Joining Eesti Elektroonikaromu: Your Partner in Responsible E-Waste Management
As one of Estonia’s most effective electronic equipment and e-waste PROs, Eesti Elektroonikaromu provides a comprehensive solution to your producer responsibilities. We handle all aspects of e-waste management on your behalf, from the collection and recycling of e-waste to reporting and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- By becoming a member of Eesti Elektroonikaromu, you can:
- Ensure compliance with the WEEE regulations and avoid potential penalties for non-compliance.
- Benefit from our extensive network of collection points and advanced recycling facilities.
- Leverage our expertise and experience to minimize your administrative burden.
- Contribute to a more sustainable Estonia by promoting responsible e-waste management.
Joining Eesti Elektroonikaromu not only fulfills your legal obligations but also demonstrates your commitment to environmental stewardship and corporate social responsibility.
Become a member of Eesti Elektroonikaromu today. Together, we can make a positive difference in Estonia’s e-waste landscape. Remember, managing e-waste responsibly isn’t just good for the environment; it’s good for business, too. Take a step towards a sustainable future with Eesti Elektroonikaromu.
Join the most effective producer
responsibility organisation in Estonia.
We collect and recycle electronics, batteries and accumulators.
We organise e-waste reporting.
Frequently asked questions on Electronic Waste Management in Estonia
E-waste, short for electronic waste, refers to discarded or end-of-life electrical and electronic devices. This includes a wide range of items, from small devices like mobile phones, laptops, and cameras to large appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and televisions. It also includes all types of discarded batteries.
Proper e-waste management is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, e-waste often contains hazardous substances, such as mercury, lead, and cadmium, which can harm the environment and human health if not disposed of properly. Secondly, e-waste also contains valuable materials, including gold, silver, and palladium, that can be recovered and reused, contributing to resource efficiency and the circular economy.
In Estonia, e-waste is managed under the principles of the EU’s Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive, which the country has adopted into its national legislation. Under this directive, the responsibility for e-waste management falls on the producers of electronic and electrical equipment. Producer Responsibility Organizations, such as Eesti Elektroonikaromu, play a significant role in helping these producers fulfill their obligations, facilitating the collection, recycling, and responsible disposal of e-waste.
You can dispose of your old electronic devices at various collection points established by Producer Responsibility Organizations like Eesti Elektroonikaromu. Alternatively, when purchasing a new device, you can return your old device to the retailer, as they are required to take back old equipment for recycling.
The collected e-waste in Estonia is processed and treated in a manner that adheres to the WEEE Directive’s guidelines. This process involves the safe removal and disposal of hazardous substances, and the recovery and recycling of valuable materials, which can then be reintroduced into the manufacturing cycle. This approach contributes to the goals of resource efficiency and sustainable development.
Related materials
- Mandatory information on producers’ and distributors’ websites on the collection of waste electronics and batteries
- Obligation to repair now as a law: the European Parliament obliges manufacturers to repair broken products
- Notification Obligation for Retailers and Online Stores in Electronic Waste Management
- Extended Producer Responsibility
- Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive
- A most effective E-Waste Recycling company in Estonia







