Quick links to article content:
WEEE Responsibilities for Manufacturers, Producers, Retailers, and Webshops
The importance of environmental responsibility and sustainable practices has gained momentum in recent years, leading to the establishment of regulatory measures worldwide. One significant directive in the European Union is the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive.
This legislation outlines the responsibilities of manufacturers, producers, retailers, and online sellers (webshops) in handling electronic and electrical waste.
Estonia, being a member of the EU, adheres to the WEEE directive, requiring all relevant stakeholders to follow specific responsibilities to ensure safe disposal and effective recycling of electronic waste. This article provides a detailed examination of these responsibilities and highlights the ways these roles contribute to sustainable practices in Estonia.
WEEE Responsibilities of Manufacturers
Manufacturers are an integral part of the WEEE directive due to their role in creating the electronics and electrical equipment that eventually become waste. Under the WEEE directive, manufacturers in Estonia are required to:
- Register their products with the relevant national authority, the Estonian Environment Agency.
- Report the amount of electronic and electrical equipment put on the market.
- Finance the collection, treatment, recovery, and environmentally sound disposal of WEEE from their own products.
- Design products in a way that minimizes waste and encourages re-use, recycling, and recovery of their products.
- Provide information about their products’ components and materials to treatment facilities.
WEEE Responsibilities of Producers
In Estonia, producers, like manufacturers, have a significant role in the lifecycle of electrical and electronic equipment. The WEEE directive requires producers to:
- Register with the national WEEE registry.
- Provide annual declarations about the type and weight of electrical and electronic equipment they have put on the Estonian market.
- Finance the cost of collection, treatment, and recycling or disposal of their own branded products at their end of life.
- Ensure products are labeled correctly with the ‘crossed-out wheeled bin’ symbol to indicate that the product shouldn’t be disposed of as unsorted municipal waste.

WEEE Responsibilities of Retailers and Dealers
Retailers and dealers act as the connection between manufacturers/producers and consumers. As such, their WEEE responsibilities in Estonia include:
- Offering a take-back service, where customers can return old equipment when buying new, equivalent items.
- Ensuring the products they sell comply with the WEEE directive’s requirements, including correct labeling and registration.
- Informing customers about the importance of separate collection of electronic waste and the potential effects of electronic waste on the environment and human health.
- Cooperating with producers and manufacturers in collection and recycling efforts.
WEEE Responsibilities of Webshops
Online sellers or webshops, have unique responsibilities under the WEEE directive in Estonia. They need to:
- Provide a clear and visible explanation to consumers about the importance of correct disposal of electronic waste.
- Ensure the products they sell comply with WEEE directive’s requirements.
- Offer a method for the return or collection of old equipment for customers within Estonia.
- Cooperate with manufacturers and producers in the collection and recycling efforts.
The WEEE directive, by outlining the responsibilities of manufacturers, producers, retailers, and webshops, plays a significant role in mitigating the environmental impact of electronic waste in Estonia. Compliance with this directive not only helps reduce harmful effects on the environment and public health but also fosters a circular economy, emphasizing sustainability, resource efficiency, and responsible consumption.
Summary
The Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) directive is a crucial environmental regulation in the EU, including Estonia. It mandates manufacturers, producers, retailers, and webshops
WEEE Responsibilities and Producer Responsibility Organizations (PROs) in Estonia
In Estonia, adherence to the WEEE Directive also involves compulsory membership in a Producer Responsibility Organization (PRO). An example of such a PRO is Eesti Elektroonikaromu.
Producer Responsibility Organizations: An Overview
PROs are organizations appointed by producers and manufacturers to undertake the recovery and recycling of electronic and electrical equipment on their behalf. These organizations serve as intermediaries, working between waste generators, waste management facilities, and regulatory authorities to ensure the effective and efficient handling of electronic waste.
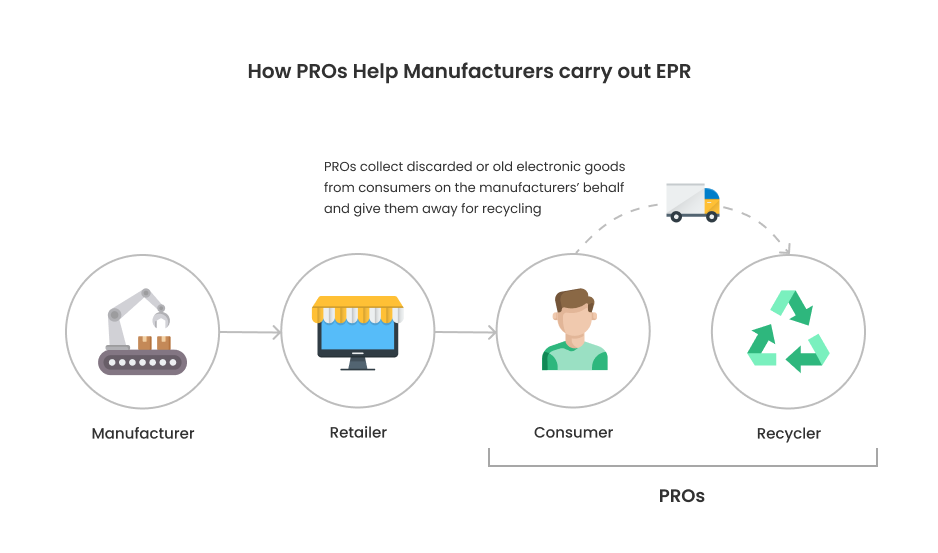
Eesti Elektroonikaromu: A Case Study
Eesti Elektroonikaromu is one of the recognized PROs in Estonia that oversees the responsible handling of electronic waste. It coordinates with manufacturers, producers, retailers, and webshops, offering solutions for WEEE management. Eesti Elektroonikaromu aids these stakeholders in fulfilling their WEEE responsibilities, such as:
- Registering products with the relevant national authority.
- Reporting the volume of electronic and electrical equipment introduced to the market.
- Financing and organizing the collection, treatment, recycling, and environmentally safe disposal of WEEE.
- Offering a take-back system for consumers to return their electronic waste.
- Providing educational material about responsible e-waste disposal.
Mandatory Membership in PROs for Companies Selling Electronic Equipment in Estonia
For companies selling electronic equipment in Estonia, joining a PRO like Eesti Elektroonikaromu is not just a matter of choice but a legal requirement.
This mandate ensures that all WEEE generated from their products is managed and disposed of responsibly. Joining a PRO offers several benefits, such as:
- Assistance in complying with complex WEEE regulations.
- Access to a nationwide network for electronic waste collection and recycling.
- Public recognition for responsible environmental behavior.
In sum, the WEEE directive plays a critical role in reducing the environmental impact of electronic waste in Estonia. As part of this directive, companies selling electronic equipment must join a PRO such as Eesti Elektroonikaromu, ensuring the proper handling, recovery, and disposal of WEEE. By joining a PRO, these companies contribute to the broader objective of promoting sustainability and a circular economy.
Summary
The WEEE directive is an essential environmental regulation in the EU, including Estonia. This directive mandates companies selling electronic equipment in Estonia to join a Producer Responsibility Organization (PRO), such as Eesti Elektroonikaromu, to ensure the correct handling and recycling of electronic waste.
This requirement not only helps these companies comply with WEEE regulations but also contributes to the promotion of a circular economy and sustainability in Estonia.
Join the most effective producer
responsibility organisation in Estonia.
We collect and recycle electronics, batteries and accumulators.
We organise e-waste reporting.
Frequently asked questions on WEEE Responsibilities for Manufacturers, Producers, Retailers, and Webshops in Estonia
The Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive is a legislation passed by the European Union (EU) to address the environmental impacts of electronic waste.
This directive places responsibility on manufacturers, producers, retailers, and webshops for the lifecycle of their products, from design and manufacturing to disposal and recycling.
The WEEE Directive is crucial because it promotes the sustainable use of resources, helps reduce electronic waste, and mitigates the potential harm to the environment and human health caused by incorrect disposal of electronic and electrical equipment.
In Estonia, manufacturers under the WEEE directive are obligated to register their products with the Estonian Environment Agency, report the volume of electronic and electrical equipment they put on the market, finance and arrange for the collection, treatment, recovery, and environmentally sound disposal of WEEE from their products.
They must also design products in a way that minimizes waste and encourages re-use, recycling, and recovery of their products, and provide information about their products’ components and materials to treatment facilities.
Retailers and webshops in Estonia must offer a take-back service where customers can return old equipment when buying new, equivalent items.
They need to ensure that the products they sell comply with the WEEE directive’s requirements, including correct labeling and registration.
They should also inform customers about the importance of separate collection of electronic waste and its potential effects on the environment and human health. Webshops, specifically, must provide a clear explanation to consumers about correct disposal of electronic waste and offer a method for the return or collection of old equipment for customers within Estonia.
Eesti Elektroonikaromu is a PRO in Estonia responsible for managing electronic waste on behalf of manufacturers, producers, retailers, and webshops.
It assists these stakeholders in fulfilling their WEEE responsibilities by helping register their products, report the volume of equipment they place on the market, finance and organize the collection, treatment, recycling, and safe disposal of WEEE.
It also helps facilitate a take-back system for consumers to return their electronic waste and provide educational material about responsible e-waste disposal.
Yes, companies selling electronic equipment in Estonia are legally required to join a PRO like Eesti Elektroonikaromu. This requirement ensures that all electronic waste generated from their products is managed, collected, treated, and disposed of responsibly in accordance with the WEEE Directive.
Related concepts and useful materials
Some key terms and references related to WEEE producer responsibility for online shops selling electronic equipment include:
WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) Directive: the EU directive on waste electrical and electronic equipment. The Directive imposes obligations on producers, sellers and importers to recover and dispose of these products.
Waste Act: the law in Estonia that regulates the generation and management of waste, including the implementation of the WEEE Directive in Estonia.
Producer Responsibility Organisation (PRO): An organisation that assists producers and sellers in meeting their obligations regarding the recovery and disposal of their products. In Estonia, one of the best known TVOs is Eesti Elektronikaromu.
Producer Responsibility: The responsibility of manufacturers, importers and sellers to ensure that their products are treated in an environmentally sound manner at the end of their life.
WEEE: Electrical or electronic equipment that has become unusable and must be recycled or properly disposed of.
References:
- WEEE Direktiiv – direktiiv 2012/19/EL
- Eesti Jäätmeseadus
- Tootjavastutusorganisatsioonide tegevuse korraldamine (Eesti Keskkonnaministeerium)
- Price List Changes Effective from 1 January 2026
- The New EU Battery Regulation
- Mandatory information on producers’ and distributors’ websites on the collection of waste electronics and batteries
- Obligation to repair now as a law: the European Parliament obliges manufacturers to repair broken products
- Notification Obligation for Retailers and Online Stores in Electronic Waste Management
- Extended Producer Responsibility






